Understanding Obesity: Causes and Solutions
Introduction
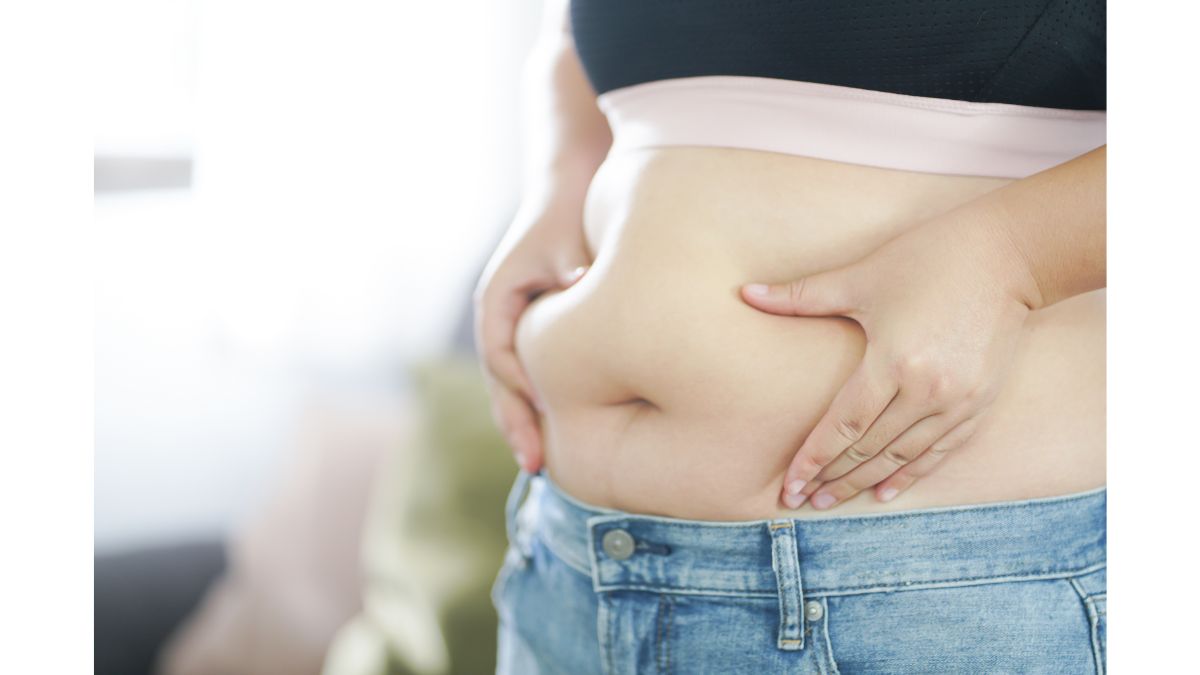
Obesity is a complicated and multidimensional health problem that has reached epidemic proportions worldwide. Obesity is defined as an excess buildup of body fat and is commonly assessed using the Body Mass Index (BMI), with a BMI of 30 or higher signifying obesity. The growth in obesity rates over the last few decades has created serious public health challenges for people of all ages and socioeconomic backgrounds.
Causes of Obesity
Obesity is the result of a combination of genetic, behavioral, environmental, and metabolic variables. Understanding the causes is critical to effective prevention and therapy.
- Genetic Factors:
- Hereditary Influence: Genetics can significantly influence an individual’s propensity to obesity. Specific genes influence how body fat is stored and distributed.
- Metabolic Rate: Genetic factors can influence an individual’s basal metabolic rate (BMR), affecting how quickly they burn calories.
- Behavioral Factors:
- Dietary Habits: A high intake of calorie-dense, nutrient-poor foods and beverages, along with big portion sizes, contributes considerably to weight gain.
- Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles, which involve little physical activity and lengthy periods of inactivity, are significant contributors to obesity.
- Environmental Factors:
- Food Environment: The availability and marketing of unhealthy foods make it challenging to maintain a balanced diet.
- Urbanization: Urban settings often promote sedentary lifestyles through reduced opportunities for physical activity and increased reliance on transportation.
- Psychological Factors:
- Stress and Mental Health: Emotional stress, depression, and anxiety can lead to overeating and poor dietary choices as coping mechanisms.
- Behavioral Disorders: Conditions such as binge eating disorder can contribute to excessive calorie intake.
Consequences of Obesity
Obesity has profound impacts on both physical and mental health, leading to a range of medical conditions and affecting quality of life.
- Health Complications:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Obesity increases the risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can lead to insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Joint Problems: The extra weight places stress on joints, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Respiratory Issues: Obesity can cause sleep apnea and other respiratory problems.
- Psychosocial Effects:
- Stigma and Discrimination: Individuals with obesity often face societal stigma and discrimination, affecting their self-esteem and mental health.
- Mental Health Disorders: There is a strong association between obesity and conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Solutions and Interventions
Addressing obesity requires a multifaceted approach, combining individual, community, and policy-level interventions.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while reducing intake of processed and sugary foods.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, and structured exercise programs.
- Behavioral Therapy:
- Counseling: Psychological counseling and support groups can help individuals develop healthier eating habits and cope with emotional triggers.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT can address underlying psychological issues contributing to obesity and promote sustainable behavior change.
- Medical Interventions:
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to support weight loss efforts.
- Surgery: Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, may be considered for individuals with severe obesity when other interventions have not been successful.
- Public Health Policies:
- Regulation of Food Marketing: Implementing policies to restrict the marketing of unhealthy foods, particularly to children.
- Urban Planning: Designing cities and communities to encourage physical activity through the creation of parks, walking paths, and bike lanes.
Conclusion
Obesity is a pressing global health issue with complex causes and serious consequences. Tackling this epidemic requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, behavioral therapy, medical interventions, and supportive public health policies. By understanding the multifaceted nature of obesity and implementing targeted strategies, we can work towards reducing its prevalence and improving the health and well-being of individuals worldwide.